Daily Current Affairs for UPSC
Global Slavery Index 2023
Syllabus- Government Policies and Interventions [GS Paper-2]
Context- The Global Slavery Index 2023, a report on the state of modern slavery in 160 nations, was published by the Walk Free Foundation.
Key Highlights
- 50 million people were living in “modern slavery” on any given day in 2021, according to the report.
- 28 million of these 50 million people are forced to work and 22 million are forced to marry. 12 million of these 50 million are children.
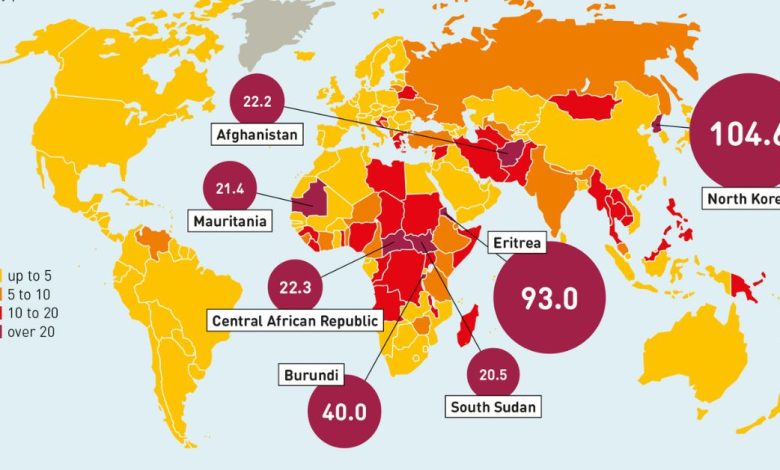
- Slavery in modern times: The percentage of modern slavery per 1,000 people is referred to as the prevalence.
- The countries with the highest prevalence are as follows: North Korea, Eritrea, Mauritania,Saudi Arabia,Turkey.
- The countries with the lowest incidence: Germany, Norway, the Netherlands, Sweden, and Switzerland
- Countries hosting the maximum number of people living in modern slavery: India, China, Pakistan, North Korea, and Russia
- The countries hosting the maximum number of people living in modern slavery account for six members from G20 nations: India, China, Russia, Indonesia, Türkiye, and the US.
What is modern slavery?
- A situation of exploitation is known as modern slavery when a person is unable to leave because of threats, violence, coercion, deception, or abuses of power.
- Abuses like forced labor, forced marriage, debt bondage, sexual exploitation, human trafficking, slavery-like practices, forced or servile marriage, and the sale and exploitation of children all fall under the umbrella term “modern slavery.”
Global Slavery Index
- The Global Estimates of Modern Slavery, which is produced by Walk Free, the International Organization for Migration (IOM), and the International Labor Organization (ILO), serves as the basis for the index, which is published by the human rights organization Walk Free.
- The estimates for 2022 serve as the foundation for this, the fifth edition of the Global Slavery Index.
Slavery-prevention initiatives
- The United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) for the World: Target 8.7 of the SDGs states: ” By 2025, stop all forms of child labor, including forced labor, modern slavery, and human trafficking, and ensure the prohibition and eradication of the worst forms of child labor, such as the recruitment and use of child soldiers.
- In 2018 Australia passed the Cutting edge Subjugation Act which requires organizations that have a combined income of over AU$100 mn per annum to cover the moves they are making to answer present day subjection.
- In accordance with the UN Trafficking Protocol, human trafficking has been made a felony in approximately 137 nations.
Steps Taken against Slavery: India
- Article 23 of Indian Constitution: It is against the law to engage in human trafficking, beggar, or other forms of forced labor that are similar to it, and breaking this rule will result in a legal violation.
- Article 24 of Indian Constitution: No child under the age of fourteen is permitted to work in a mine or factory or in any other hazardous occupation.
- Two fundamental ILO Conventions concerning the elimination of child labour, the Minimum Age Convention, 1973 (No. 138) and the Worst Forms of Child Labour Convention, 1999 (No. 182) has been ratified by India.
- The 1976 Bonded Labor Abolition Act: It stipulates that State Governments are responsible for establishing vigilance committees and prohibits bonded and forced labor. In 1985, contract and migrant workers were included in an amendment to the Act.
- Central program for Bonded Labor Rehabilitation: The rescued person receives financial assistance from it.
Concerns
- Absence of clear definition:’Modern subjection’ is a made-up idea with no global lawful definition.
- Methodology for ranking: Qualitative analysis is not taken into account by the index’s statistics.
- This ranking of nations stigmatizes poorer nations and absolves richer nations of responsibility for issues like human trafficking.
Recommendation
- Execution of more grounded measures and regulations that keep state run administrations and business from obtaining labor and products connected to present day bondage.
- Incorporating anti-slavery measures into climate change sustainability plans, providing children with primary and secondary education, and tightening regulations regarding forced and child marriage are additional suggestions.





.png)



